Failover without the fuss
Without failover, DHCP can be a single point of failure on your network. If you have a single server and it becomes unavailable, clients will be unable to request or renew IP address leases. As your reliance on your network grows, this disruption to DHCP becomes less tolerable.
Up to now, achieving solid high availability DHCP has been frustrating for network admins, surprisingly so given how universal the need is:
- A number of options, like entry-level switches and routers, don't offer any failover anyway.
- Historically, the mainstream DHCP server options did not do a great job on failover. They either had no failover options, or they were clunky to manage and didn't always work properly:
- Windows Server – despite its popularity – has historically had limitations in its failover capabilities. Its Active-Passive redundancy introduces a single point of failure, and older versions may ensure DHCP service availability but lack IP address continuity. Some versions are even restricted to IPv4 address spaces with no support for IPv6.
- Implementing failover on open-source DHCP servers can be an annoying headache. ISC's DHCPd requires expert DHCP knowledge and complicated workarounds. Its more modern successor, ISC KEA, uses a relational database that supports high availability, but early releases of this proved buggy. Setting this up with open-source tools is still hard to get right.
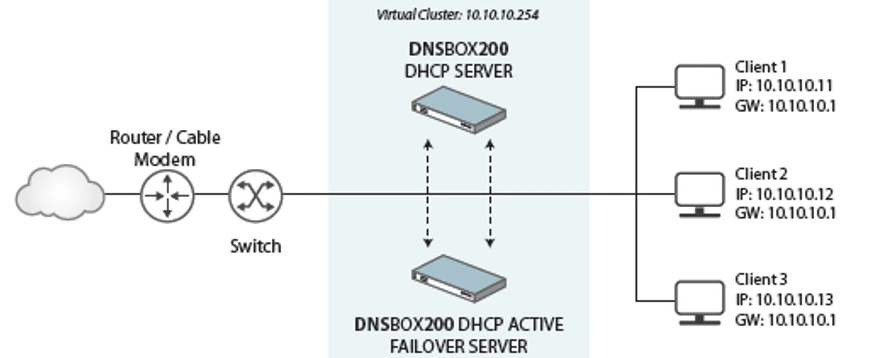
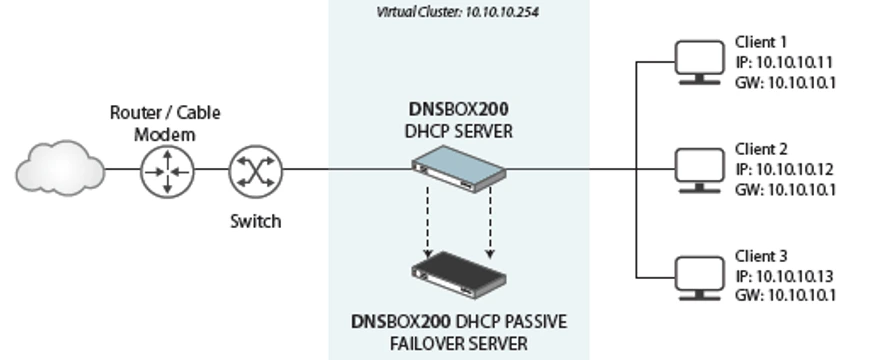
To address these frustrations, we've refined DHCP failover on DNSBOX, making it easier than ever to achieve high availability and minimize downtime with just a few clicks. DNSBOX200 failover pairs share configuration, ensuring that they never 'disagree' about the network. They also dynamically share available addresses, and information about current leases.
DNSBOX failover be set up in a few simple clicks with options to suit different network topologies and requirements.
 I love a product that just does what it's supposed to do with minimum fuss – a redundant, reliable DHCP service.
I love a product that just does what it's supposed to do with minimum fuss – a redundant, reliable DHCP service.